The WatsonCrick model of DNA structure Watson & Crick constructed a model of DNA structure that fits Franklin's Xray diffraction data & Chargaff's rules The basic unit of nucleic acid structure is the nucleotide a 5carbon sugar molecule called ribose covalently linked to a nitrogenous base at the 1' carbon, and a phosphate at theDNA Structure Activity Problem 10 Features of the WatsonCrick Model for DNA structure Which of the following is correct about the WatsonCrick model of DNA?Structure has novel features which are ofconsiderable biological interest A structure for nucleic acid has already been proposed by Pauling and Corey' They kindly made their manuscript available to us in advance of publication Their model consists of three inter twined chains, with the phosphates near the fibre axis, and the bases on the outside In our opinion, this structure is

Dna Structure Watson Crick Franklin And Wilkins Youtube
Watson crick model of dna structure
Watson crick model of dna structure-Although the globally accepted structure is known as the Watson and Crick model of DNA structure, one important person left out of the historical teaching of DNA's discovery is Rosalind Franklin The data of this female British biophysicist was critical to Watson, Crick and Wilson's work, which would earn them a Nobel Prize for the discovery Franklin was not eligible for theThe WatsonCrick Model of DNA Structure STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by meckels001 Terms in this set (5) The Model a)Hydrogen bonds hold complementary base pairs together in DNA b)Two DNA strands form a double helix c) Four turns of a DNA double helix double helix ladderlike structure that's twisted Antiparallel two strands in a DNA




Watson And Crick S Model Of Double Helix Of Dna Biochemistry
Watson and Crick used many aluminium templates like this one, which is the single base Adenine (A), to build a physical model of DNA in 1953 When Watson and Crick produced their double helix model of DNA, it was known that most of the specialized features of the many different life forms on Earth are made possible by proteinsDNA's Structure The model of DNA that they proposed look like none before, consisting of a doublehelix structure very similar to an extension ladder · Watson and Crick DNA Model DNA Model The threedimensional structure of DNA, first proposed by James D Watson and Francis H C Crick in 1953, The Nitrogen Bases or Nucleotides DNA strands are composed of monomers called nucleotides These monomers are often Deoxyribose Sugar Deoxyribose,
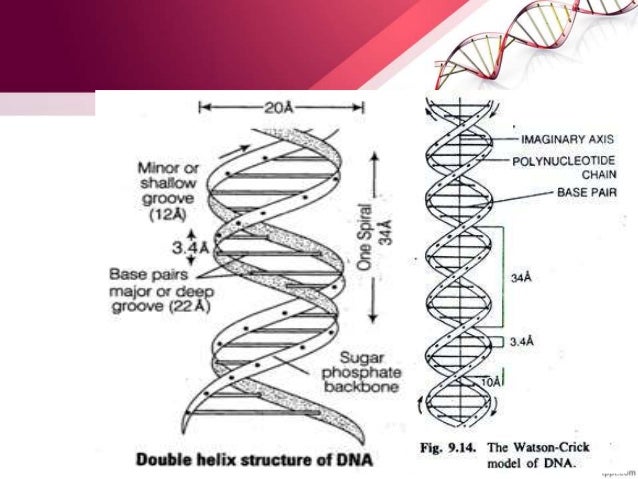
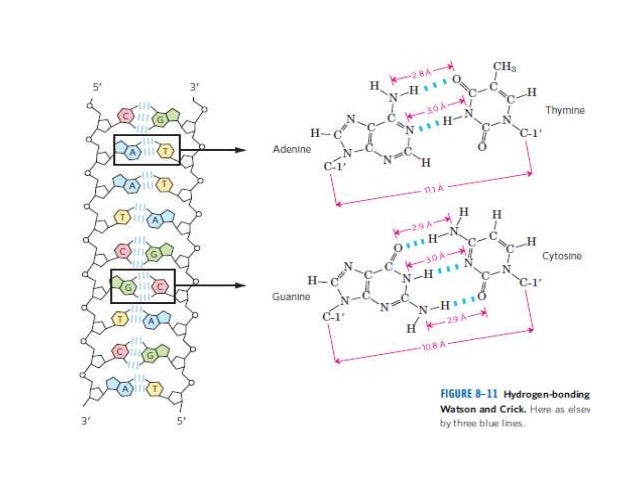
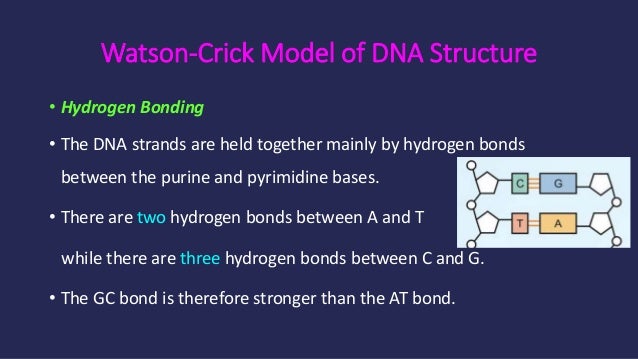
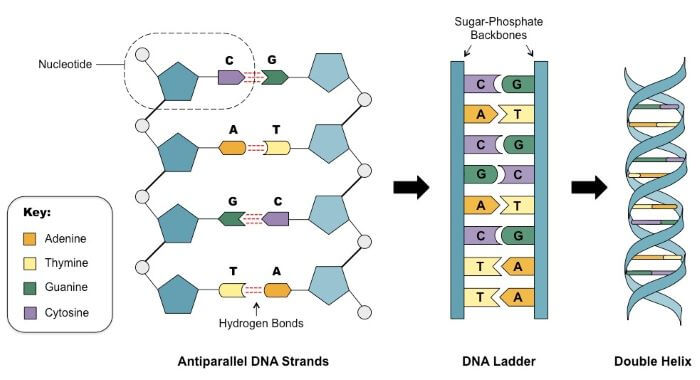
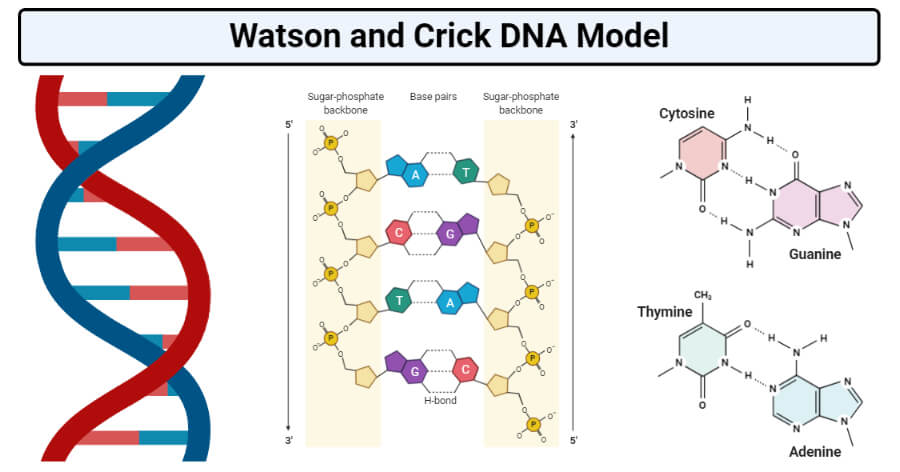
#structure of dna#watson & crick's model#nucleoside#nucleotide#nucleic acid#adinine#guanine#thymine#cytosine#purine#pyramidine#deoxy ribose · In 1953, JD Watson (an American biologist) and FHC Crick (a British Physicist) proposed the threedimensional model of physiological DNA (i e BDNA) on the basis of Xray diffraction data of DNA obtained by Franklin and Wilkins For this epochmaking discovery, Watson, Crick and Wilkins got Nobel Prize in medicine in 1962A model of DNA structure in which the molecule is a crosslinked doublestranded helix, each strand is composed of alternating links of phosphate and deoxyribose, and the strands are crosslinked by pairs of purine and pyrimidine bases projecting inward from the deoxyribose sugars and joined by hydrogen bonds with adenine paired with thymine and with cytosine paired with
Phobeus Levene proposed the Tetra nucleotide theory and Linus Pauling's triple helix model Both these even though wrong provided many clues regarding the DNA structure; · Watson and Crick's Model for DNA JDWatson and FHC Crick (1953) combined the physical and chemical data, and proposed a double helix model for DNA molecule This model is widely accepted According to this model, the DNA molecule consists of two strands which are connected together by hydrogen bonds and helically twisted · Watson and crick model of dna 1 Watson and Crick model of DNA 2 Watson and Crick model of DNA Some Basic Nucleoside is a compound formed by the combination of a pentose sugar and 3 Nitrogen bases present in DNA 1 Adenine 3Cytosine 2 Guanine 4Thyrosine The different types of nucleosides




Solved 52 In The Watson Crick Model Of Dna Structure A Chegg Com



Dna The Thread Of Life Watson Crick Model Characteristics 2
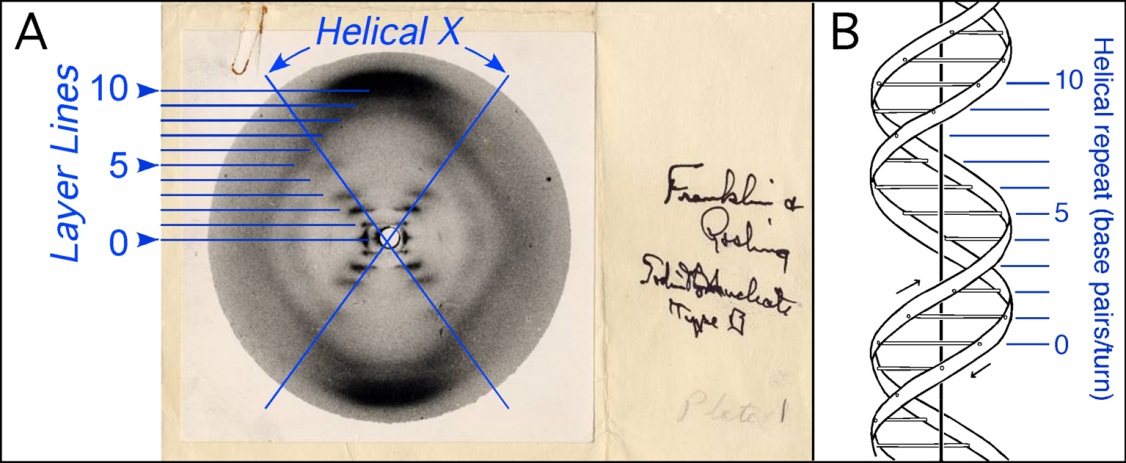
Structure of DNA (DNA double helix) Watson Crick Model Class 12thSubject BiologyChapter Molecular Basis of Inheritance Topic Name Structure of DNA or Watson and Crick model of DNAA model of DNA structure in which the molecule is a crosslinked doublestranded helix, each strand is composed of alternating links of phosphate and deoxyribose, and the strands are crosslinked by pairs of purine and pyrimidine bases projecting inward from the deoxyribose sugars and joined by hydrogen bonds withWatsonCrick were undoubtedly the first to propose an essentially correct model for DNA structure, a wide vari ety of available data was used by them to arrive at this 'canonical' model for DNA, in particular the nucleotide base composition data of Chargaff (Table 1) and informa tion from the Xray fibre diffraction pattern (Figure 2) of



Watson And Crick Model Of Dna




Watson Crick Model Of Dna Hindi Urdu Youtube
DNA Structure Watson and Crick's model of DNA The structure of DNA was a mystery before the 1950s It was at the beginning of 1950s, James Watson (American biologist) and Francis Crick (British physicist) after combining the available physical and chemical data and based on their research introduced the doublehelix model for DNADNA is a double helical structure consisting of two long strands, coiled around a ventral axis This structure was discovered by Watson and Crick Each strand is a polynucleotide chain, composed of many nucleotides Each is formed by a pentose, deoxyribose sugar, a/05/19 · Watson and Crick model of DNA provides one of the best ways to demonstrate the structure of doublehelix DNA A DNA is a polymer composed by the combination of several monomer units (deoxyribonucleotides) linked by the phosphodiester bond In the discovery of DNA, many scientists have contextualized the structure of DNA, its components and composition etc




The Story Of Dna Discovery Youth Stem 30



Structure Of Dna
The secondary structure of DNA B form, or Watson and Crick's model Two complementary dinucleotides pair their bases to form a fragment of doublestranded BDNA 5' pTpC 3' 3' ApGp 5' The base pairs are positioned in parallel and internal, while pentoses and phosphates (backbone) are external In order to have all the bases paired, while keeping the phosphodiester bonds, each · Watson and Crick thus envisaged the structure of DNA molecule as a kind of twisted ladder, the two upright consisting of chains of alternating sugar and phosphate groups, the rungs as pairs of bases sticking inwards towards each other and linked up in a specific relationship A with T and C with G They then proceed to build molecular models · In late 1951, he and Watson combined that theory with what they knew about the chemistry of DNA, and what they remembered of talks given by Wilkins and Franklin, to build a model of the DNA structure



Dna Structure Alphabet Soup For The Cellular Soul Intechopen




Structure Of Dna Watson Crick Model Of Dna Biology 12th Chapter Youtube
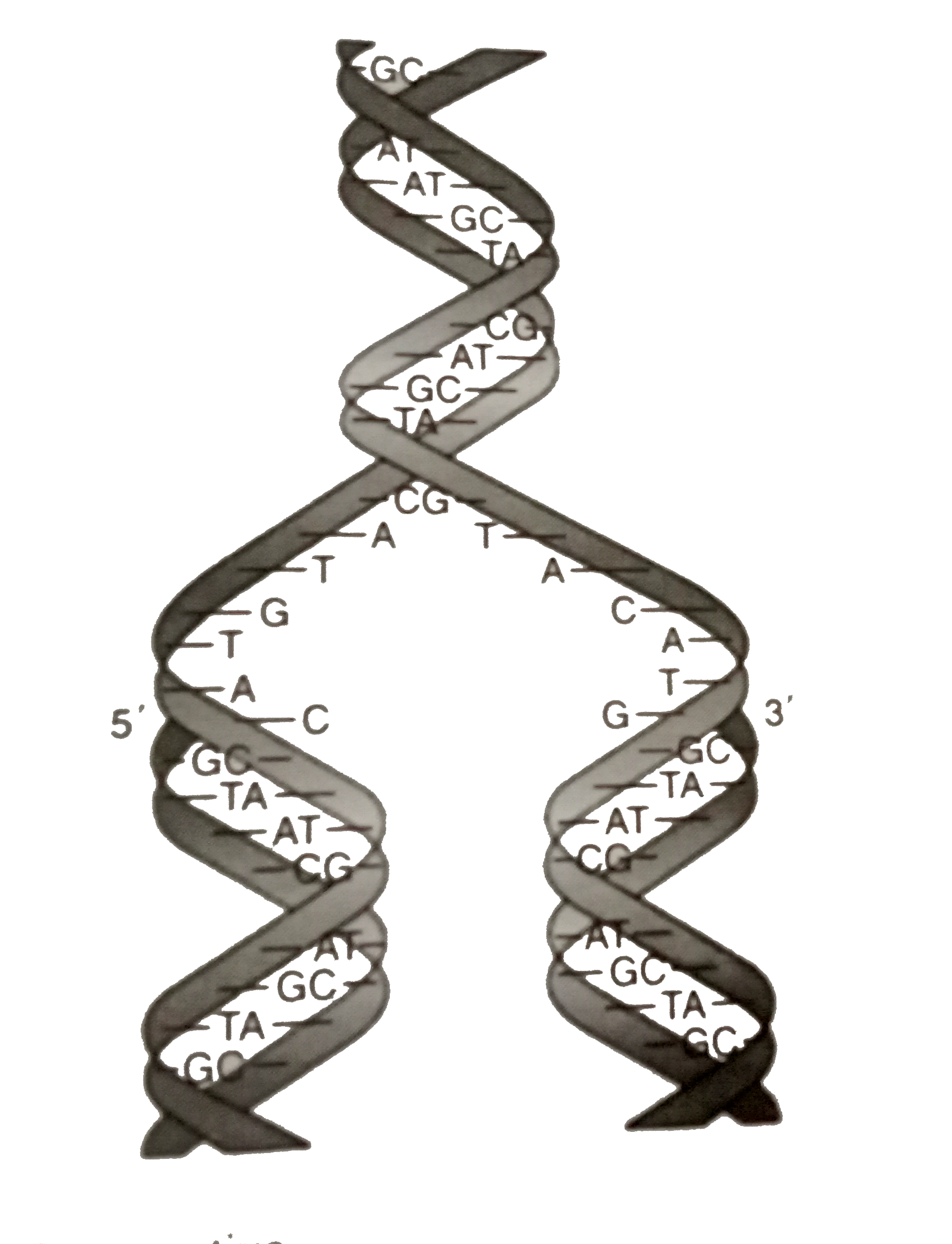
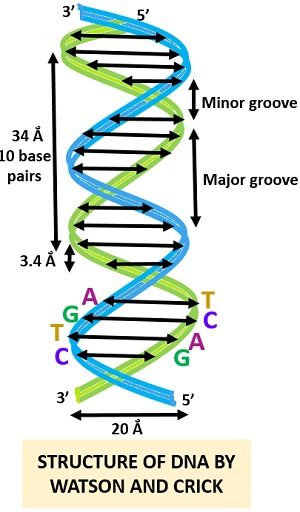
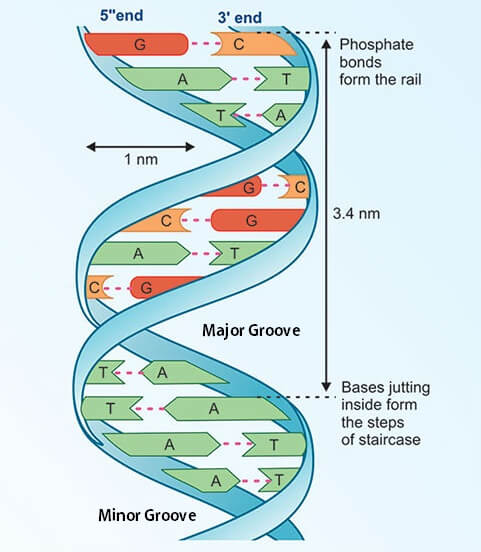
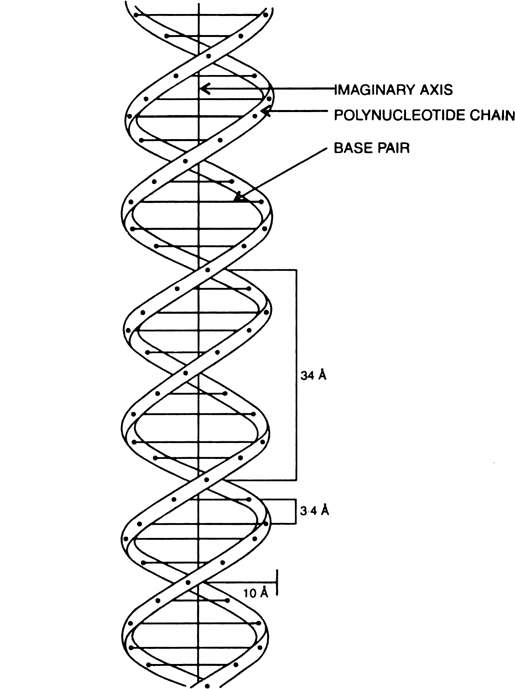
Transcribed image text In the WatsonCrick model of DNA structure, both strands are parallel, run in the same direction, 3' 5' the distance between two adjacent bases in one strand is about 34 A nitrogencontaining bases are on the outside of the helix, where they can form Hbond with water OHbonds and hydrophobic stacking are forces to hold two single strand DNA to double strand DNA · Chemical structure of DNA discovered On February 28, 1953, Cambridge University scientists James D Watson and Francis HC Crick announce that they have determined the doublehelix structure ofThe WatsonCrick Model of DNA (1953) Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) is a doublestranded, helical molecule It consists of two sugarphosphate backbones on the outside, held together by hydrogen bonds between pairs of nitrogenous bases on the inside The bases are of four types (A, C, G, & T) pairing always occurs between A & T, and C & G
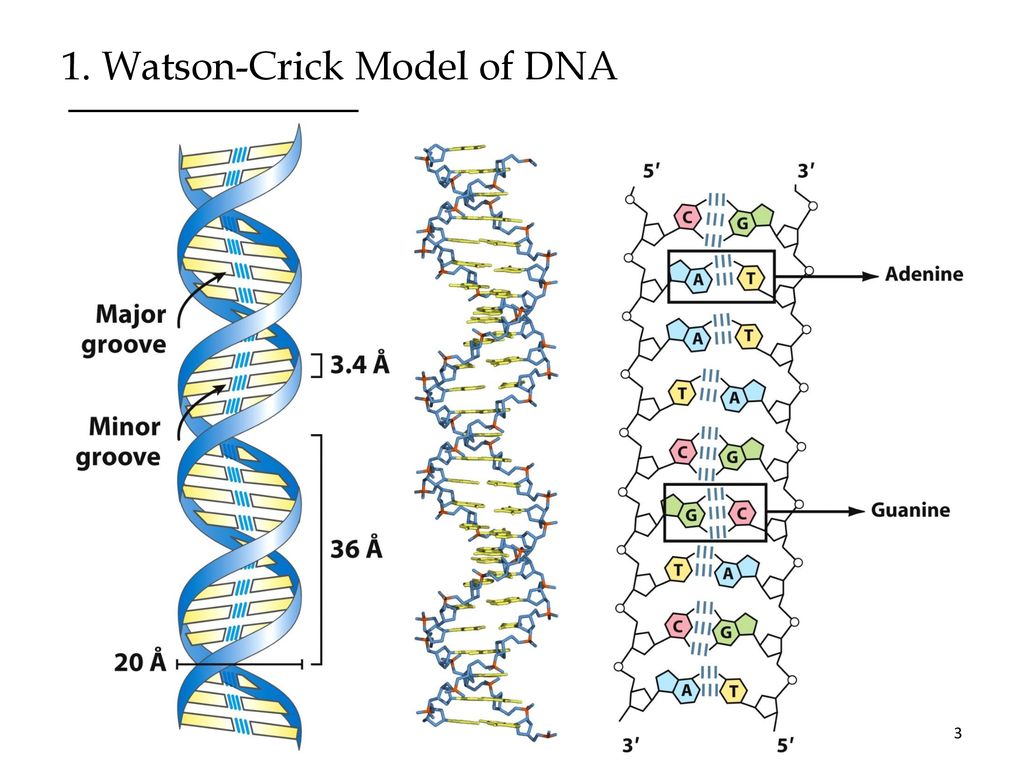



Nucleic Acid Structure And Stability Ppt Download




Chargaff S Complimentarity And Watson Crick S Model Of Dna Structure
Part 2 The WatsonCrick model of DNA structure Watson & Crick constructed a model of DNA structure that fits Franklin's Xray diffraction data & Chargaff's rules The biochemist Erwin Chargaff analyzed the base composition of DNA from a wide variety of species, and found that although the percentages of Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thymine varied from species to · Watson and Crick (Double Helix) model of DNA James Watson and Francis Crick has made a major contribution in 1953 to the development of the structure of DNA They combined the physical and chemical data and proposed DNA as double helical twisted molecules connected together by hydrogen bonds DNA is a backbone for all life and this model hasAny proposed model for DNA must be capable of forming either Structure V GENETICAL IMPLICATIONS OF THE A or Structure B and so it remains imperative for COMPLEMENTARY MODEL our very tentative interpretation of Structure A to be confirmed As a preliminary we should state that the DNA fibers from which the Xray diffraction patterns (2) The anomolous titration




Watson And Crick S Model Of Double Helix Of Dna Biochemistry



Describe The Watson And Crick Model Of Dna Structure With A Diagram Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
A) Each strand contains all the information present in the double helix B) There are structural and functional similarities between DNA and RNA C) The double helix is righthanded, not left handed D) DNA replication does not require enzyme catalysts · WatsonCrick Model of DNA Structure • Right Handed Double Helix • DNA consists of two polydeoxyribonucleotide chains twisted around one another in a right handed double helix • The bases are located perpendicular to the helix axis, whereas theDNA structure Revisiting the Watson –Crick do u ble helix Manju Bansal Institute of Bioinformatics and Applied Biotechnology, ITPL, Bangalore 560 066, India and Molecular Biophysics Unit, Indian Institute of Science, Ba ngalore 560 012, India Watson and Crick's postulation in 1953, exactly 50 years ago, of a double helical structure for DNA, he ralded a revolution in our understanding of




Describe Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna




Structure Of Dna Watson And Crick Model Replication Significance
The doublehelix model of DNA structure was first published in the journal Nature by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, (X,Y,Z coordinates in 1954) based on the work of Rosalind Franklin, including the crucial Xray diffraction image of DNA labeled as "Photo 51", from 1952, followed by her more clarified DNA image with Raymond Gosling, Maurice Wilkins, Alexander Stokes, andReconstruction of the double helix model of DNA, using some of the original metal plates, by Francis Crick and James Watson, England, 1953 In 1953, the British and American molecular biologists Francis Crick and James Watson pulled off one · Watson and crick Model of DNA The Molecular Structure of DNA was proposed by Watson and crick Watson and Crick (1953), based on Xray diffraction method, proposed a double helical model of DNA to explain molecular structure of DNA for which they got Nobel prize in 1962 The main points of model are given below Each molecule of DNA consists of two helical




Tertiary Dna Structure As Represented In Watson And Crick S Model Is A Download Scientific Diagram




Bits And Bytes Of Biology Watson And Crick Model Of Dna
The April 25, 1953 issue of Nature published Crick and Watson's 900word article, "A Structure for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid" Wilkins and Franklin, who both accepted Crick and Watson's solution, wrote accompanying articles By the 1960s scientists generally embraced the double helix as the structure of DNA, and in 1962 Wilkins, WatsonThe backbone of each DNA strand is a repeating sugarphosphate polymer The strands of DNA are antiparallel, spiraling around the helix axis in opposite directions The sequences of bases in the two strands areIn DNA molecule the adjacent deoxyribonucleotides are joined in a chain by phosphodiester bridges or bonds which link the 5 carbon of the deoxyribose of one mononucleotide unit with the 3 carbon of the deoxyribose of the next mononucleotide unit



Dna Structure Function Watson And Crick Model Chargaff S Rule




Dna Structure
Useful notes on Watson and Crick's Structural Model of DNA ! · Watson and Crick model of the DNA double helix Courtesy of Science Source Images After looking through Franklin's data, Watson and Crick were able to find that the DNA structure was a double helix with antiparallel strands, which meant that the strands ran in opposite directions By discovering the DNA strand directions, they just needed to find the appropriateThey proposed the threedimensional model of DNA on the basis of Xray diffraction studies of DNA obtained by Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins In appreciation of their discoveries on the molecular structure of nucleic acids Watson, Crick and Wilkins were awarded Nobel prize for Medicine in 1962 Chemical Composition of DNA molecule DNA is a large molecule consisting of




Discovery Of Dna Double Helix Watson And Crick Learn Science At Scitable




Watson And Crick Model Of Dna Biology Q A Doubtnut
· WatsonCrick Model A model of DNA structure in which the molecule is a crosslinked doublestranded helix, each strand is composed of alternating links of phosphate and deoxyribose, and the strands are crosslinked by pairs of purine and pyrimidine bases projecting inward from the deoxyribose sugars and joined by hydrogen bonds · Watson and Crick proposed the model of DNA According to the model, DNA is helical and made of two strands with about uniform width of 2 nm DNA contains all information for the synthesis of proteins Thus, DNA is the basic source of hereditary informationIn the WatsonCrick model of DNA structure (now called Bform DNA) a) a purine in one strand always hydrogen bonds with a purine in the other strand b) AT pairs share three hydrogen bonds c) GC pairs share two hydrogen bonds d) the 5' ends of both strands are at one end of the helix e) the bases occupy the interior of the helix




Double Helix Dna Model By Watson And Crick




Knowledge Class Watson And Crick Model Of Dna
· The history of Watson and Crick's proposed DNA model is controversial and a travesty of scientific ethics Rosalind Franklin was deeply involved in the determination of the structure of DNA, and had collected numerous diffraction patterns Watson attended a departmental colloquium at King's College given by Franklin, and came into possession of anErwin Chargaff of Columbia University proposed the complementarity of base pairing Summary of Watson and Crick model 1) The DNA molecule is composed of two chains of nucleotides 2) The two chains spiralMoreover, he had pioneered the method of model building in chemistry by which Watson and Crick were to uncover the structure of DNA Indeed, Crick and Watson feared that they would be upstaged by Pauling, who proposed his own model of DNA in February 1953, although his threestranded helical structure quickly proved erroneous The time, then, was ripe for their discovery




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica




Structure Of Dna
Watson and Crick describe structure of DNA 1953 Photo Model of DNA molecule In the late nineteenth century, a German biochemist found the nucleic acids, longchain polymers of nucleotides, were36 Which feature of the Watson–Crick model of DNA structure explains its ability to function in replication and gene expression?Answer The following points explain the model of DNA as proposed by Watson and Crick 1 DNA is made up of double helix made up of polynucleotide chains that are coiled with each other in a righthanded fashion 2 The two strands are antiparallel to each other One stand runs in 5'3' polarity and other runs in 3' to 5' polarity
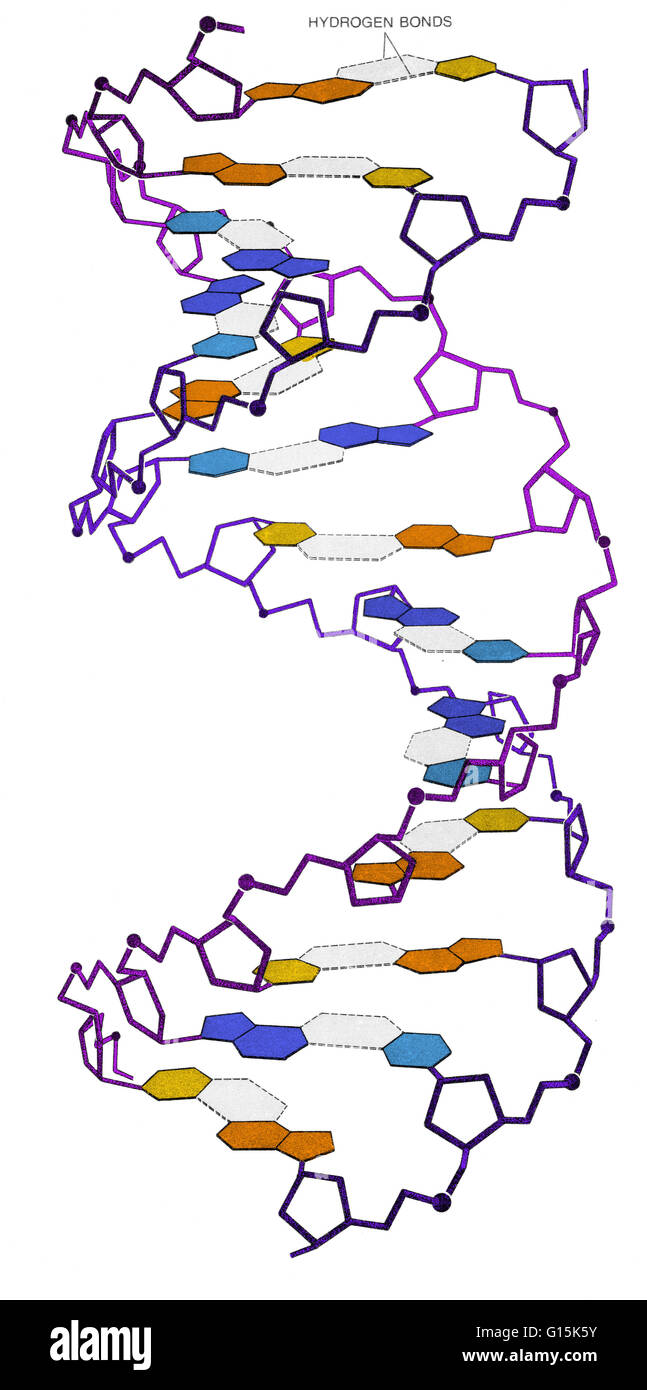



Color Enhanced Image Of The Watson Crick Model Of The Structure Of Dna The Discovery Of Which Was Announced In 1953 And Led To Their Winning The Nobel Prize According To The Watson Crick




Structure Of Dna




Watson Crick Structure Of Dna




Dna Structure Watson Crick Franklin And Wilkins Youtube




Detail The Watson Crick Model Of Dna Structure How Did It Fit In The Data Provided By Chargaff Ignou Notes
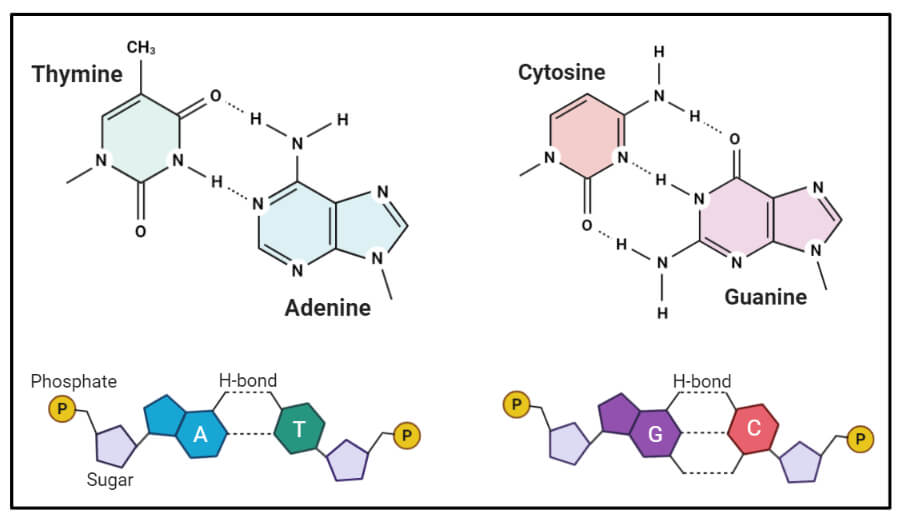



Watson And Crick Dna Model Molecular Biology Microbe Notes
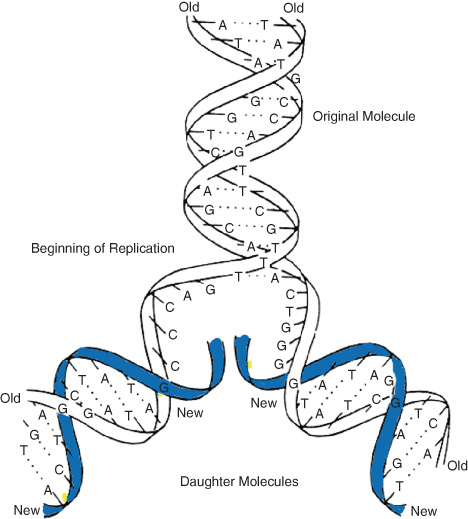



Watson And Crick Model Springerlink




Crick And Watson S Dna Molecular Model Science Museum Group Collection




A False Start



Dna Structure Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Javatpoint




Molecular Structure Of Nucleic Acids A Structure For Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid Wikipedia




Structure Of Dna Molecule Proposed By Watson And Crick




Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Double Helix Watson Crick Model Of Dna Structure Nucleic Acid Structure And Function Mcat Content



The Watson Crick Model Of Dna Exhibits Of Dna Biology Q A Doubtnut




Pgc Lectures Watson Crick Model Of Dna Youtube Dna Model Dna Model




Structure Of Dna



7 1 Dna Structure And Replication Ppt Download




Welcome To Class Of Dna Dr Meera Kaur




Watson And Crick Model Of Dna Full Explain The Structure Brainly In




7 Watson And Crick Visuals Addison Ideas Dna Chemical Structure Biology




Dna Structure By The Early 1900s It Was



Watson And Crick Model Of Double Helix Of Dna Mim




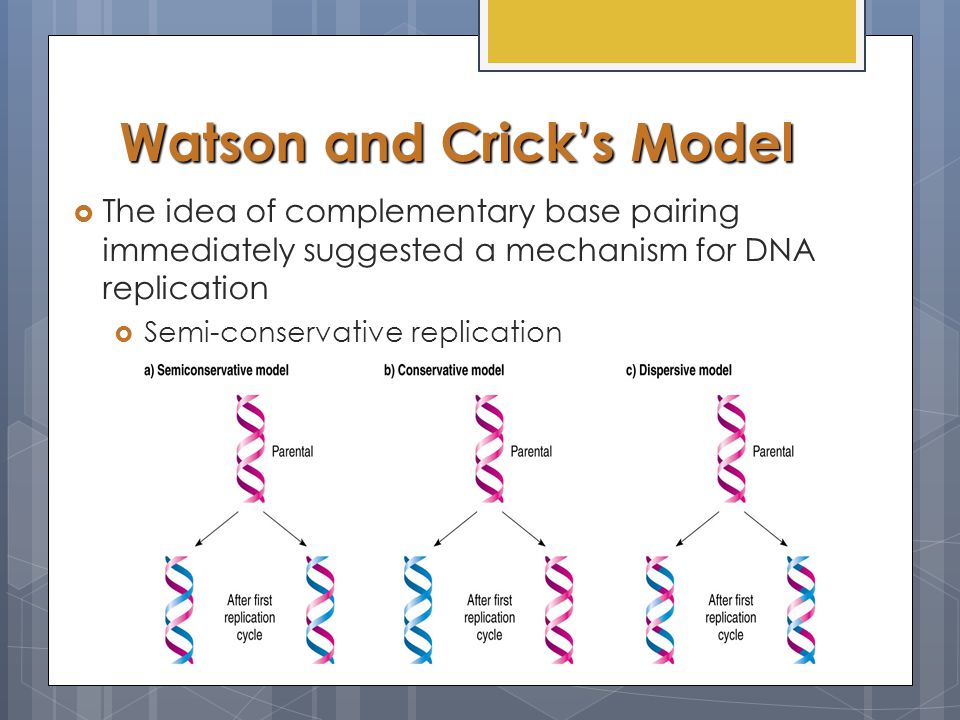
Which Property Of Dna Double Helix Led Watson And Crick To Hypothesise Semi Conservative Mode Of Dna Replication Explain Target Batch




Watson And Crick Model Of Dna Assignment Help



Describe The Double Helix Model Given By Watson And Crick Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community




Science Class 8th Ch 02 Watson And Crick Model Of Dna Youtube



Watson And Crick S Original 3 D Demonstration Model Of Dna Download Scientific Diagram




Dna Replication Using The Watson And Crick Dna Model Easyhsc




Ladder Structure Of Dna Showing The Watson Crick Bonding Of The Bases Download Scientific Diagram




Dna The Language Of Evolution Francis Crick James Watson




With The Help Of A Neat And Labelled Diagram Describe Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Biology Shaalaa Com




Deoxyribonucleic Acid Dna Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader
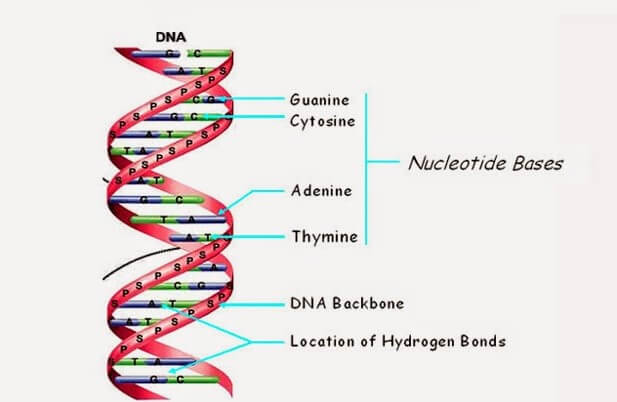



Dna Structure Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Javatpoint




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader




Pdf Dna Structure Revisiting The Watson Crick Double Helix Semantic Scholar




Dna The Thread Of Life Watson Crick Model Characteristics




Obsolete Models Of Dna Structure Wikipedia




Watson Crick Bioninja
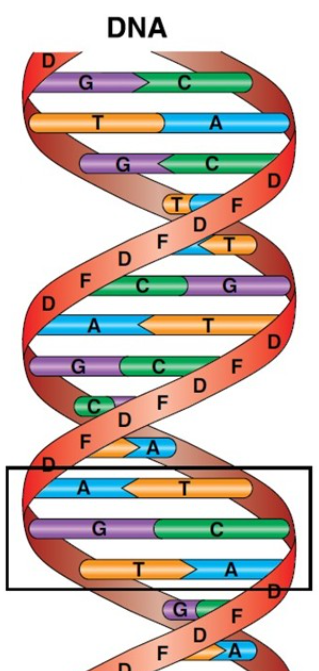



Explain Watson And Crick Model Of Dna Class 12 Biology Cbse



Watson And Crick Dna Model Molecular Biology Microbe Notes




Learn Salient Features Of Watson And Crick Model In 3 Minutes




Watson Crick Model Banque D Image Et Photos Alamy



Explain Watson Crick Model On Dna Structure Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
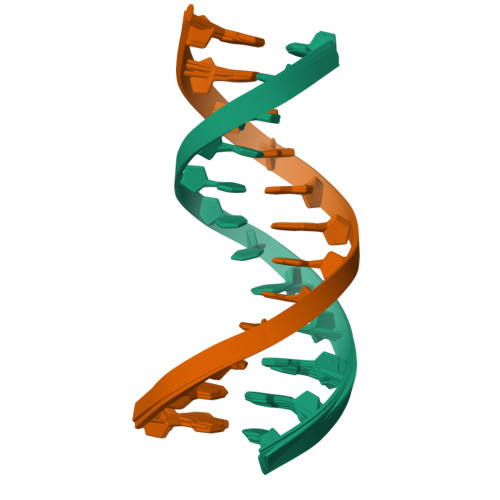



Rcsb Pdb 5uzf Insights Into Watson Crick Hoogsteen Breathing Dynamics And Damage Repair From The Solution Structure And Dynamic Ensemble Of Dna Duplexes Containing M1a A6 Dna Structure




Dna From Watson And Crick To Modern Molecular Biology
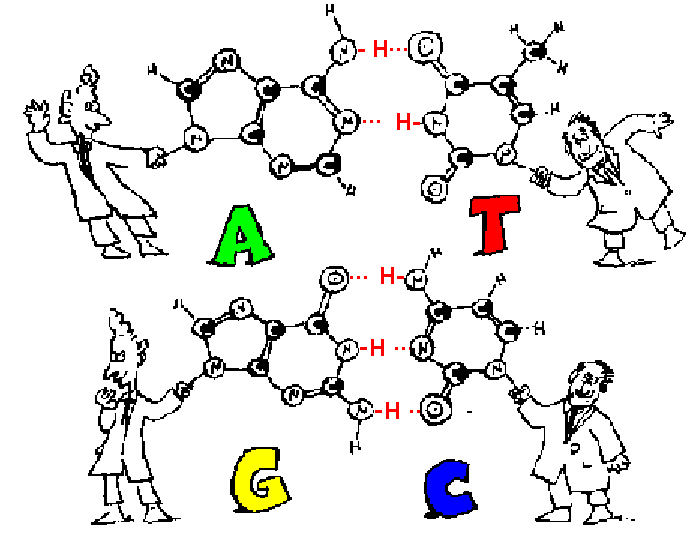



Watson Crick Structure Of Dna




Chargaff S Complimentarity And Watson Crick S Model Of Dna Structure
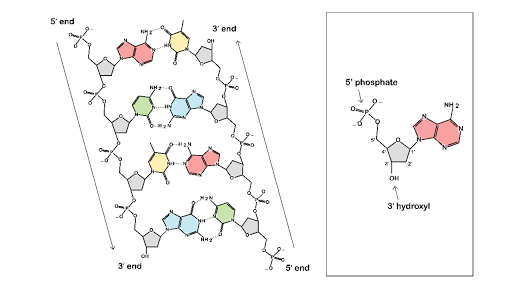



Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy




Watson And Crick S Original Model Of The Double Helical Structure Of Dna And Rosalind Franklin S Crystallograph Of The S Photograph 51 Model Rosalind Franklin
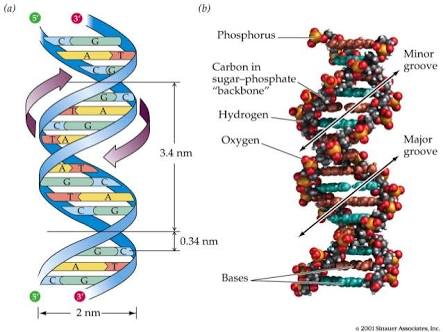



Question 151c8 Socratic




Learn About Base Pairing In Dna The Watson Crick Model Chegg Com




Page 3 10 Bio 15 Newflip



How Dna Replicates Genetics How Dna Replicates




Pin On Learning Biology




The Structure Of Dna Genetics The Structure Of Dna




Chap 8 A Nucleotides And Nucleic Acids Some



Watson And Crick S 3d Model Of Dna
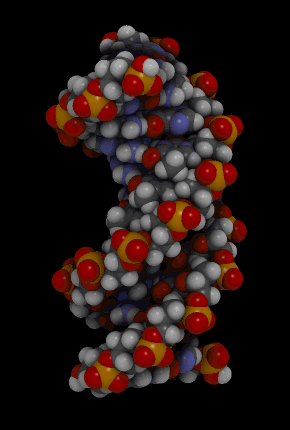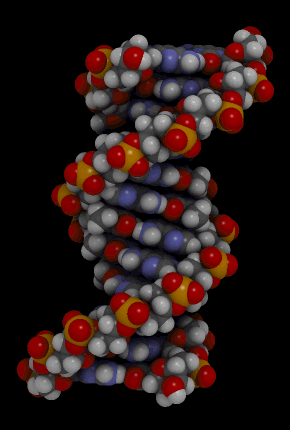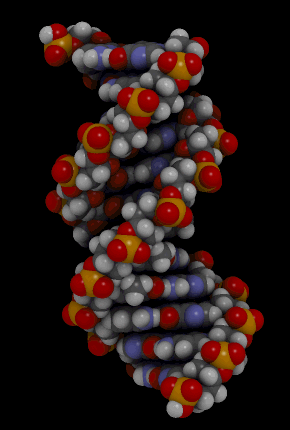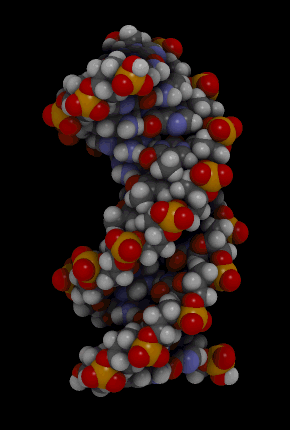



Discovery Of The Structure Of Dna Article Khan Academy




Crick And Watson S Dna Molecular Model Science Museum Group Collection




Dna Structure And Function Watson And Crick S Dna Model Ppt Download



Exe




The Watson Crick Model Of Dna Exhibits Of Dna Biology Q A Doubtnut



Dna Structure Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna Javatpoint




Watson And Crick 1953 Double Helix Model Of Dna Ppt Download




Watson Crick Model Of Dna Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Standard Note Watson And Crick S Model Of Dna




Heredity Structure And Composition Of Dna Britannica




Basic Dna Structure Proposed By Watson And Crick Dna Is Made Up Of Two Download Scientific Diagram



Describe Watson And Crick Model Of Dna From Biology Biomolecules Class 11 Cbse




Symmetry Free Full Text Symmetry In Nucleic Acid Double Helices Html




Figure 1 From A Glossary Of Dna Structures From A To Z Semantic Scholar




Watson Crick Model Of Dna Structure Reprinted By Permission From Download Scientific Diagram




The Watson And Crick Structure Of Dna Dna Tattoo Dna Art Dna Model


